
The yolk albumen egg white and shell. Keep them warm and to feed them as follows.
Caring for Your Ducklings After They Hatch.
Duck development in egg. There the egg develops from the inside out starting with the yolk – this serves as a food source for the duck throughout his development and around which the first cells form. These cells are called the gastrula and over the course of the ducks incubation they will develop to form the different parts of his body like his lungs muscles nerves and skin. Each egg has all the vital components needed to produce a new life in the form of a developing embryo a duckling and ultimately an adult duck capable of producing its own eggs.
Besides self-maintenance and survival virtually everything else that waterfowl do in the months leading up to spring is focused in some way on nesting and the eggs that are produced. Baby duck breeds go through a number of development stages on their way to adult ducks. They incubate and develop in the egg.
When ducklings hatch from the egg they need care and protection from predators. Around six weeks they develop oil. They lay their eggs in batches of about 20.
The first few eggs of the first batch will be small and they should not be set for incubation. Ducks usually begin laying at about 67 months of age and should be laying at a rate of about 90 ie. The growth and development of the duck egg after a few days of its fertilization form a half-formed duckling inside it.
This half-formed duck is called a duck embryo. The eggshells of such fertilized duck eggs have partially formed duck embryos. These eggs are allowed to incubate for at least 18 days to create the embryo.
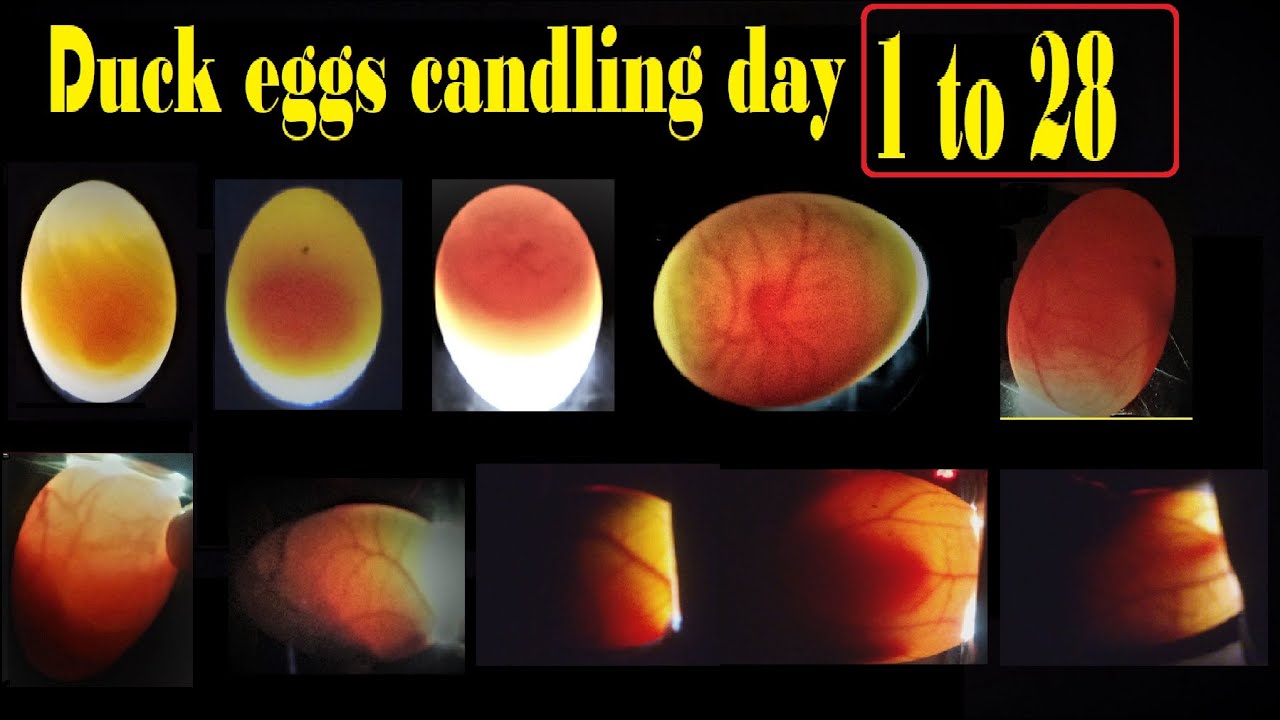
Egg teeth gradually thicken and the egg teeth of the duck embryo have the deposition of pigment. Nictitating membrane shields anterior scleral papillae and approaches the cornea. Embryonic development of the duck goose and chicken at stages 36 to 40.
Descriptions refer to Figure 7. Bar 1 cm. The fertilized embryonic disc looks like a ring.
It has a central area lighter in color which is to house the embryo. The germinal disc is at the blastodermal stage. The segmentation cavity under the area pellucida takes on the shape of a dark ring.
Eggs can be held for about a week before incubation without a problem. The ideal holding temperature is about 60 degrees. A refrigerator is too cold.
Development of the embryo only begins when the egg is warmed to the correct temperature. Caring for Your Ducklings After They Hatch. Keep them warm and to feed them as follows.
Duck eggs have to be kept at very specific humidity levels to hatch and those levels vary depending on the stage of egg development. Momma duck instinctively knows this information and her feathers are ideal for providing just the right levels of moisture so long as she has access to swimming water. During week two the feathers begin to form along with the egg tooth a special part of the bill used during hatching that falls off shortly after the duckling hatches.
Week 3 brings the rest of the feathers. A hardening of the beak scales and claws. And continued development of the organs.
Read also. Development Duck Salted Eggs Part 2. Initially this salted egg business was done hereditary and pioneered by some locals as a part-time business.
With their skills they have the idea to preserve eggs to be durable and have high economic value. Their skill in processing the salted egg industry is not only so but requires a long process. Incubate Duck Eggs and Duck Embryo Development.
Water loss occurs inside of the duck egg as the duckling embryo grows and takes up more space. The air cell inside of the eggshell will increase as the water cell decreases. Fertile raw duck eggs.
The sorting of an intact duck egg with a crack is characterized by the difference in the sound of the collision of two eggs slowly. If the sound of ting-ting means the duck egg is intact and passes sorting while the sound of tech is a sign that the duck egg has been damaged. An egg consists of three main parts.
The yolk albumen egg white and shell. Everything a duckling needs for its development is contained within these three components. The yolk consists of fat protein vitamins and minerals while the albumen is primarily protein.
The trick for those of you at home candling duck eggs in these later stages of the incubation period is to shine the light in through the blunt end of the egg where the air cell is - I could see the most amazingly clear shadow of the little ducklings and was even able to distinguish the eye and the bill from the head last night. My duck eggs from first stages of growth to hatching - YouTube. If playback doesnt begin shortly try restarting your device.
If we talk about the chick development in biological terms then the major stages are worth noticing. The egg when laid after almost 20 hours of fertilization undergo few chicken egg developmental stages. The egg laying is followed by cleavage which is again followed by gastrulation which then leads to organogenesis and this eventually leads to hatching chicken.
The life cycle of ducks includes several stages. Ducks incubate and hatch from eggs. They are protected by the mother duckling until they are ready to molt and migrate to a warmer climate.
The next year they then return to their birthplace to. My first impression of the inside of the duck egg that had been developing for almost 3 weeks was that the substance inside the egg was suprisingly sticky. I dont know if its always the case or it was sticky because of the cracks and some sort of rotting process.
Animation of the 21 day development of a chicken embryo in the eggCreated by AXS Biomedical Animation Studio Inc. Duck egg white was mixed with sodium hydroxide to produce translucent alkali-induced egg white jelly similar to that in preserved egg whites. To develop a heatable translucent egg white jelly their physiochemical properties and thermal stabilities were investigated.
Effects of dietary lysine supplementation on performance egg quality and development of reproductive system in egg-laying ducks Ahmed Mohamed Fouadab Wei Chena Dong Ruana Shuang Wanga Weiguang Xiaa and Chuntian Zhenga aInstitute of Animal Science Guangdong Academy of Agricultural Science Key Laboratory of Animal Nutrition and Feed Science South.