The main function of the lungs is the process of gas exchange called respiration or breathing. Respiratory system of frog parts and Functions.

When frog is more active during locomotion swimming in water during leaping and jumping the demand of oxygen increased.
Lungs function in a frog. What Is The Function Of The Lungs In A Frog. Once mature frogs lose their gills and are able to bring oxygen into their bodies through functioning though comparatively underdeveloped lungs. Frogs rely on their lungs to breathe when they are active and need more oxygen than skin respiration alone can provide.
What is the function of the lungs. The main function of the lungs. What Is The Function Of The FrogS Lungs.
Once mature frogs lose their gills and are able to bring oxygen into their bodies through functioning though comparatively underdeveloped lungs. Frogs rely on their lungs to breathe when they are active and need more oxygen than skin respiration alone can provide. What is the function of the lungs.
The main function of the lungs. Frog lungs work in a similar way to the lungs of other mammals bringing in oxygen and breathing out carbon dioxide. However frogs dont have a diaphragm so they bring air into their throat sac and force it down into the lungs instead.
The main function of the lungs is the process of gas exchange called respiration or breathing. In respiration oxygen from incoming air enters the blood and carbon dioxide a waste gas from the metabolism leaves the blood. Also Know what is the function of the pancreas in a frog.
The pancreas of frog produces enzymes into the small intestine to help breakdown the. The function of the frog lungs is to facilitate the supply of oxygen in the body. They allow adult frogs to breathe in without using their skin.
The lungs are used to. A frogs lungs provide adult frogs the ability to breath not only through their skin but to also be able to inhale oxygen through their nostrils. The mechanism of taking air into the lungs is however sligthly different than in humans.
Frogs do not have ribs nor a diaphragm which in humans helps serve in expand the chest and thereby decreasing the pressure in the lungs allowing outside air to flow in. The lungs are not only the organs of respiration but are also hydrostatic organs as they enable frog to float in water when they are inflated. Pulmonary respiration and sound production in frog.
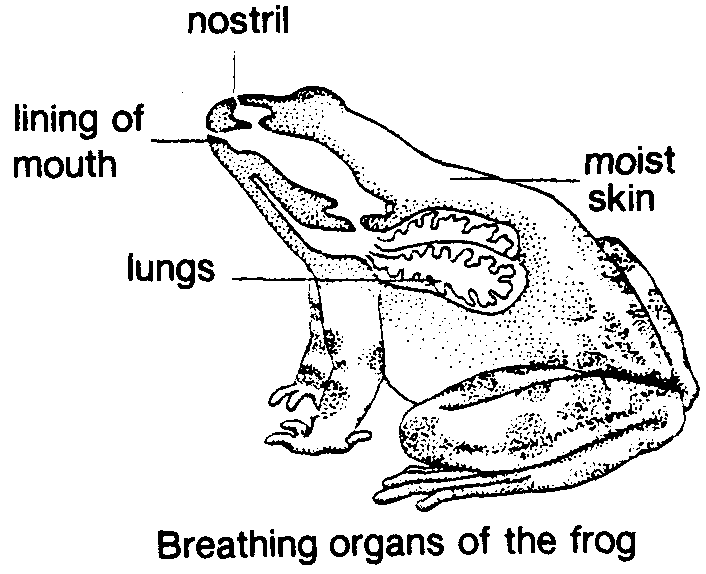
The breathing that takes place on land in the atmospheric air by the help of lungs is termed as pulmonary respiration. In case of frogs the lungs are poorly developed. Thus the insufficient supply of O 2 obtained through lungs is supplemented by the moist skin and buccal cavity.
Functions of the Frog Heart Right Atrium - Chamber of the frogs heart which receives blood from the sinus venosus. Left Atrium - The chamber of the heart that receives blood from the lungs. Pulmonary Veins - The blood vessels that carry blood form the lungs to the left atrium.
Ventricle - Chamber of a frogs heart that pumps. These organs are the lungs. They are located under both the heart and liver They are spongy like structures.
Their function is to allow the frog to breathe by collecting the air in their lungs and then releasing them. This is the gall bladder. The gall bladder is a.
Frog respires through lungs when it lives on land. When frog is more active during locomotion swimming in water during leaping and jumping the demand of oxygen increased. For pulmonary respiration the routes of air passages are as follows.
Pulmonary respiration takes place by lungs when the frog is on land. The lungs are a pair of elongated or oval thin walled pinkish elastic sacs. Their inner lining is raised to form many chambers called alveoli which increase the inner surface for exchange of gases.
The alveoli are separated from each other by septa. Respiratory system of frog parts and Functions. Respiration in tadpole of frog occurs by means of gills as in fishes.
In adult frog due to its amphibian life respiration occurs through skin cutaneous respiration lining of the bucco-pharyngeal cavity buccal respiration and the lungs pulmonary respiration Pulmonary Veins - The blood vessels that carry blood form the lungs to. Opening to the lungs. Frog can breath through these with its mouth closed can be opened or closed with sphincter muscles.
Opening to the typanum eardrum typanum tympanic membrane or eardrum serves to equalize pressure within. What are the different parts and functions of the respiratory system in frogs. Frogs breathe using their skin lungs and mouth.
However they breathe through their skin most of the time. The frogs moist and thick skin absorbs oxygen through the blood vessels present on the skin surface allowing for gaseous exchange on water and land. As amphibian larvae develop the gills and in frogs the tail fin degenerate paired lungs develop and the metamorphosing larvae begin making excursions to the water surface to take air breaths.
The lungs of amphibians are simple saclike structures that internally lack the complex spongy appearance of the lungs of birds and mammals. Erythrocytes of frog blood provide it with a pink color while in humans it is bright red. Connecting in the lungs with oxygen they carry it to every cell of the body where they give it up and attach carbon dioxide.
The latter comes in the opposite direction and exhales. Erythrocytes also transport amino acidscarrying out a nutritional function. Cloaca - Organ through which the products of the frogs digestive and urogenital system pass when discharged from the body.
Anatomy of a Frog Heart Functions of the Frog Heart Heart - Pumping organ of the circulatory system has 3 chambers. Anterior Vena Cava - Large vein that carries blood from the anterior part of the body toward the heart. These two types of nostrils work together to provide oxygen to frogs when theyre not in the water.
In addition to nares frogs can also. Ventricle - Chamber of a frogs heart that pumps blood out of the heart to the lungs and other parts of the body. Truncus Arteriosis - Large artery in a frog that carries blood away from the ventricle into branches that lead to all parts of the body.
Urinary System Frog Brain Functions of the Frog Brain Spinal Cord - Main pathway to and. Similarly it is asked what is the function of a frogs lungs. When the frog is out of the water mucus glands in the skin keep the frog moist which helps absorb dissolved oxygen from the air.
A frog may also breathe much like a human by taking air in through their nostrils and down into their lungs. What is the function of the frogs heart. The Frog Heart The atrium receives deoxygenated blood from the blood vessels veins that drain the various organs of the body.
The left atrium receives oxygenated blood from the lungs and skin which also serves as.