A final pathway for hepatocyte copper is excretion into the bile. Or an even larger dog we can come from behind beneath the legs and palpate like that.

Typically the range for normal AST is reported between 10 to 40 units per liter and ALT between 7 to 56 units per liter.
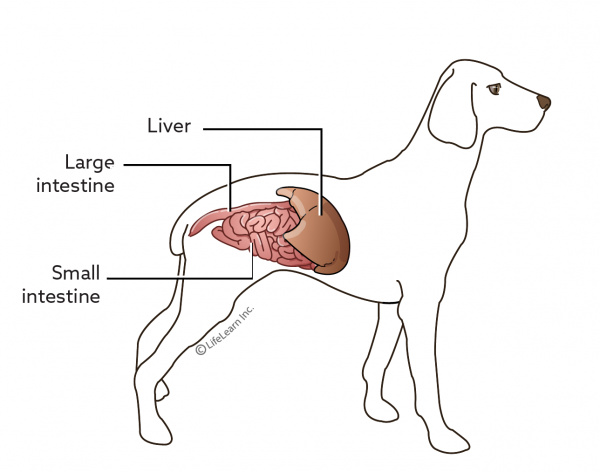
Normal canine liver. A dogs liver has many responsibilities. Breaking down toxins before they enter the body removing waste products from the blood storing energy and giving blood the ability to clot. While the liver is enormously resilient–it can continue to function even after large portions have been removed–the levels of enzymes present in this critical organ can serve as a gauge of your dogs overall health.
Top best answers to the question What is normal liver enzyme count in dogs. Answered by Liza Treutel on Tue Mar 30 2021 848 PM. Typically the range for normal AST is reported between 10 to 40 units per liter and ALT between 7 to 56 units per liter.
Mild elevations are generally considered to be 2-3 times higher than the normal range. The normal range for the alanine aminotransferase or ALT enzyme which is liver specific is 10-100 UL according to the Canine Liver Disease Foundation. Elevated ALT enzymes are usually due to cell damage caused by leakage.
To determine the effects of selective transcatheter arterial embolization TAE in the normal canine liver. Adult Beagle dogs n 5. Gelatin sponge particles GSPs were injected through a microcatheter for selective embolization of the left hepatic artery in normal dogs.
EXAMINATION OF NORMAL CANINE LIVER VESSELS. Timothy MWANZA Toru MIYAMOTO Masahiro OKUMURA Mitsuyoshi HAGlO and Toru FUJINAGA. 13 1996 ABSTRACT The aim of this study is to provide a description of the ultrasonographic and angiographic anatomy of the hepatic and portal veins in normal dogs.
Ultrasound of a normal canine liver. Left aspect of the liver on a sagittal view. The liver has a homogenous parenchyma and is hypoechoic to the spleen S.
The portal vessels white arrow have hyperechoic walls. Healthy Dog Liver Enzyme results. Liver enzymes are shown on blood tests as a number with a normal range next to them this normal range represents the expected levels seen in the vast majority of cases.
If your animal has normal liver enzymes we would expect them to be as shown below. A serum biochemistry panel is performed with the results in Table A. The fasted ammonia concentration is 175 mcgdL normal range 050 mcgdL.
Preprandial and postprandial 2-hour SBA are 40 mcmolL normal 08 mcmolL and 102 mcmolL normal 030 mcmolL respectively. The liver lies entirely within the costal arch appearing small. The gastric axis is perpendicular to the spine a normal variation for a dog with deep thoracic conformation.
The distal extremity of the spleen lies immediately caudal to the liver. C Lateral radiograph of the abdomen of a normal cat. There is individual variation in the size of the normal liver in the dog and the cat making the distinction between a mildly enlarged or mildly small liver from a normal liver highly subjective and relatively inaccurate.
The position of the stomach is one parameter that is commonly used as an indicator of liver size. Its not uncommon for the ALT levels to vary widely from dog to dog and most vets will not be alarmed unless your pets ALT levels are at least 3 times the normal rate on multiple readings. AST A slight increase in the enzyme AST can be indicative of very serious liver problems like cirrhosis and cancer.
Contrastenhanced ultrasonography a new imaging modality in veterinary medicine can provide data on tissue perfusion. The objective of this study was to use the ultrasonographic contrast agent SonoVue to evaluate various transit time indices in the normal canine liver to examine the effect of anesthesia on these parameters and to evaluate the safety of this agent. The Normal Canine Abdominal Exam Exam 3.
Be able to just feel the edge of the liver here. Up under here and then move dorsally and feel up under. Smaller dog come with one hand palpate like this.
Or an even larger dog we can come from behind beneath the legs and palpate like that. Dogs30 The high MT content of normal canine liver is unexplained. A final pathway for hepatocyte copper is excretion into the bile.
The biliary system is the major route of excretion of copper from the body. Several pathways in the hepatocyte have been shown to contribute cop-per to the biliary pool including lysosomal exocytosis. In this dog the liver margins come to a point arrow and are seen ventral near field relative to the stomach A.
This finding is normal. In another dog the margins of the liver lobe are rounded and seen caudal to the stomach B. This is an indication of increased hepatic volumesize.
Normal canine liver stained with desmin antibody. A A HSC right is positive in the perinuclear cytoplasm weakly extending into a cytoplasmic process. Also a negative vitamin A-storing HSC.
Contrast-enhanced ultrasonography a new imaging modality in veterinary medicine can provide data on tissue perfusion. The objective of this study. Chapter 6 - Morphological classification of parenchymal disorders of the canine and feline liver.
Normal histology reversible hepatocytic injury and hepatic amyloidosis. Select Chapter 7 - Morphological classification of parenchymal disorders of the canine and feline liver. Hepatocellular death hepatitis and cirrhosis.
Aspirates from a normal canine left and feline right liver. Majority of nucleated cells are large polygonal epithelial cells hepatocytes in clusters that have finely granular basophilic cytoplasm black arrows. The other liver enzymes always seem to be behaving its just this one thats wonky.
The normal range depends on the lab your veterinarian uses but most consider anything up to 130 or so as normal. Its not a shock at all to see a dog have an Alk-P of 200 even 400. The effect of selective transcatheter arterial embolisation TAE using trisacryl gelatine microspheres TGMs in the normal canine liver was investigated.
Selective embolisation was achieved by injecting TGMs into the left hepatic artery. The effect of selective transcatheter arterial embolisation TAE using trisacryl gelatine microspheres TGMs in the normal canine liver was investigated. Selective embolisation was achieved by injecting TGMs into the left hepatic artery through a.